I frequently get questions about specific injuries. Many of these are about plantar fasciitis. Here is a breakdown of one of the more common causes of plantar fasciitis.
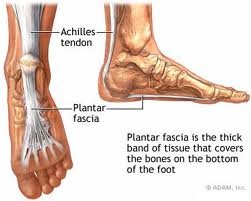 Plantar fasciitis is a pain symptom located at the heel or plantar fascia of the foot–the thick connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It is often most painful in the morning with the first steps out of bed, and may be aggravated by standing, walking, or running.
Plantar fasciitis is a pain symptom located at the heel or plantar fascia of the foot–the thick connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It is often most painful in the morning with the first steps out of bed, and may be aggravated by standing, walking, or running.
Here’s the deal about plantar fasciitis
It is the diagnosis of symptoms. It is not the diagnosis of the problem. The pain may be in your foot–but the problem is not. What you will not often find in definitions or explanations of plantar fasciitis on the web is that there is a deeper issue at play. The pain in your foot diagnosed as plantar fasciitis can often be traced back up to your gluteus maximus–your butt. These days, we sit too much and our butts muscles wind up not doing much. So they basically shut down or go to sleep–they become inhibited. This is not a good thing.
Your gluteal muscles have some very important functions. They are some of the most powerful muscles in the body and are the primary reason we stand upright. The gluteus maximus is a pelvic stabilizer and powerful hip extensor. The gluteus maximus provides power when we are going upstairs, rising from a sitting position, and climbing or running.
 Hip extension is your ability to stand upright. If you look at our primate cousins who still use their hands to walk, you’ll notice they have tiny butts. They also lack the ability to extend their hips into a fully upright standing position. Pelvic stability is hugely important. It provides the ability to stabilize the pelvis to our upper body, support the low back, and provide a solid powerful core. This point where your pelvis stabilizes with your upper body is where most coordinated movement is generated. If you lack pelvic stability, your entire movement system will be negatively affected. Your body demands stability. Without it, your body will find compensation elsewhere, by utilizing other muscles to do the job of those that are “sleeping,” i.e. inhibited. With plantar fasciitis, the calves are recruited to help stabilize the pelvis. This is not the work the calves are functioned to do. They don’t like it. Move like this long enough, and your calves will turn into The Incredible Hulk–they will get very angry and start to smash, i.e. tighten up and cause big hurt.
Hip extension is your ability to stand upright. If you look at our primate cousins who still use their hands to walk, you’ll notice they have tiny butts. They also lack the ability to extend their hips into a fully upright standing position. Pelvic stability is hugely important. It provides the ability to stabilize the pelvis to our upper body, support the low back, and provide a solid powerful core. This point where your pelvis stabilizes with your upper body is where most coordinated movement is generated. If you lack pelvic stability, your entire movement system will be negatively affected. Your body demands stability. Without it, your body will find compensation elsewhere, by utilizing other muscles to do the job of those that are “sleeping,” i.e. inhibited. With plantar fasciitis, the calves are recruited to help stabilize the pelvis. This is not the work the calves are functioned to do. They don’t like it. Move like this long enough, and your calves will turn into The Incredible Hulk–they will get very angry and start to smash, i.e. tighten up and cause big hurt.
How this translates into pain in the foot
The two muscles that we call the calves (Gastrocnemius and Soleus) attach to the heel via the Achilles Tendon. The Achilles Tendon wraps over the heel bone where it then becomes the Plantar Fascia. The Plantar fascia stretches across the bottom of the foot to the base of your toes. While we may think of these muscles and tendons as separate 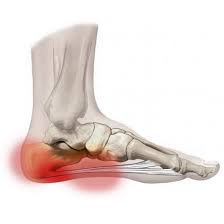 tissue structures, you can see by the picture that these structures are not separate. They are one continuous fascial tissue structure. So you can imagine that tension in one will affect each of the others. If your calves are working overtime–doing not only their job but also the job of your glutes–they may get distressed. With this distress, inflammation and pain will eventually set in. That pain can then show up anywhere in this continuous tissue chain. When the pain appears at the heel or plantar fascia, we call it plantar fasciitis. If it happens above the heel, it is called Achilles Tendonitis or tendonosis. The irony of all this is that the calves are not the issue! If anything, they are the most functional muscle in the group–they’re working overtime, after all. It’s their relationship with the asleep at the wheel Gluteals which need to be addressed. This is where the pain in your foot is literally a pain in the butt.
tissue structures, you can see by the picture that these structures are not separate. They are one continuous fascial tissue structure. So you can imagine that tension in one will affect each of the others. If your calves are working overtime–doing not only their job but also the job of your glutes–they may get distressed. With this distress, inflammation and pain will eventually set in. That pain can then show up anywhere in this continuous tissue chain. When the pain appears at the heel or plantar fascia, we call it plantar fasciitis. If it happens above the heel, it is called Achilles Tendonitis or tendonosis. The irony of all this is that the calves are not the issue! If anything, they are the most functional muscle in the group–they’re working overtime, after all. It’s their relationship with the asleep at the wheel Gluteals which need to be addressed. This is where the pain in your foot is literally a pain in the butt.
Relieving plantar fasciitis pain
When treating any kind of painful dysfunction, my first goal as a movement specialist is to help my clients find relief from the pain. The method I’ve found most beneficial for this is self massage using The Grid foam roller to release the tension built up in the calves. Here are some simple exercises to help relieve the discomfort in your foot by working with The Grid.
Now once the pain is gone, this does not mean you are fixed. Pain is a communicator–it alerts us to an underlying problem. But it is not the problem itself. This is why the “treatments” often found online (such as this one) will only provide temporary relief; they target the symptom (pain) rather than the core underlying issue.
There is still movement dysfunction that needs to be assessed and addressed, and as detailed above, it likely originates in the hips. Strengthening and balancing movement patterns associated with the glutes is the next step in treating plantar fasciitis, and can best be done by making an appointment with a qualified movement specialist. To ignore this step places you at risk of an even more painful and serious injury at some point in the future. Finding help is hugely important in the long run for continued recovery and pain free movement.
Here are some simple quick tips for quick temporary relief. Or check out this older article with more exercises to help with plantar fasciitis pain.

Using a foam wedge, press heel into the ground and actively straighten your knee. Stretch to slight discomfort, NOT pain. Hold for 1-3 minutes each stretch
This is the foam roller I recommend: The Grid by Trigger Point Therapy



I had suggested to me that running backwards for a few intervals would help with PF and it did with me. I also used a foot roller called footlog that helped with the pain and tension in my arches. I’m sure there are more exercises and tools to help but these both helped fix my issue.
Good article! Enjoyed learning new facts vs. myths.
Thanks Laura.
Great article! I’m a Pilates instructor and I always have my clients roll out the bottoms of their feet before we begin our workout. I do this for two reasons. One is to help break up the bound fascia and two is to help with proprioception. Dr. Janda states that our proprioception begins at the bottom of our feet.
Thanks Cassidy.